Alvados depression
Share Image
-
Alvados depression
-
Lisboa e Vale do Tejo
-
Porto de Mós
-
Serras de Aire e Candeeiros Nature Park
Identification and Access
-
No
-
Access to Alvados coming from:
- Alcanena (± 19.7 km) – N365 and N243;
- Porto de Mós (± 7.5 km) – N243 to Alvados/Santo António.
GPS: 39.557550, -8.781461
Base Characterization
-
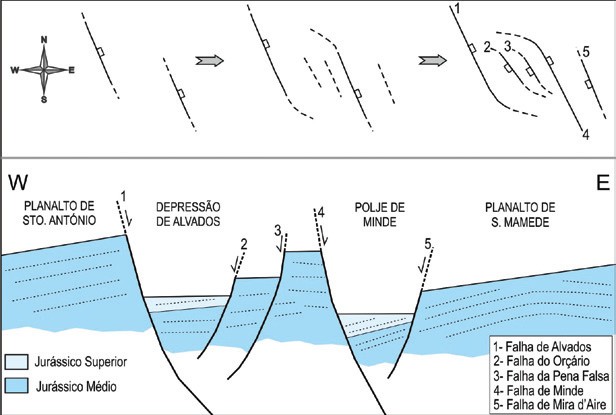
Tectonic depression bounded to the West by the scarp of Alvados fault and to the East by the fault of Pena Falsa, both oriented NW-SE. On the south part, the depression is limited by the fault of Sto. António with W-E orientation. In a simplistic way, it is a basin with a wide flat bottom, with an immense carpet of olive trees that timidly climb along the extensive and uniform Alvados hills, as it is called the 300 m slope that reaches the plateau of Santo António. This is one of the most beautiful landscapes of this massif.
Its genesis is conditioned by the normal movement of the fault system of Alvados and Minde during distensive period of the Upper Jurassic period. It led to the depression of the block located between Alvados and Pena Falsa faults. Later in the Paleogene, the landforms have been accentuated by the movement of the strike slip fault with a thrust component of the two limitrophe faults oriented NW-SE and the reverse movement of Sto. António’s fault. To the latter are associated folds that contributed to accentuate the landforms.
Depression – landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area.
Fault –Cracks in the Earth's crust where movement occurs on at least one side.
Fold – formed when one or several originally flat and planar surfaces, such as sedimentary beds, become bent or curved as a result of plastic (e.g. permanent) and ductile deformation.
Jurassic - geological period in which the dinosaurs dominated and the development of vegetation was abundant. It lasted about 54 million years, roughly between 208 to 144 million years ago.
Paleogene - beginning of the Cenozoic Era. It began 65 million years ago (My) and lasted until 23.5 My. Includes the Paleocene, the Eocene and the Oligocene periods.
Strike slip fault –when the movement of blocks along a fault is horizontal.
Tectonics - study of rocks deformation that make up the Earth's crust and the forces that produce such deformation.
Thrust - formed by horizontal compressive stresses and so cause shortening of the crust. Because the hangingwall moves up relative to the footwall, most of these faults place older rocks over younger ones.
-
Local
Infrastructures

Instituto da Conservação da Natureza e das Florestas, I.P.
Karst Route
Lisbon and Tagus ValleyLisbon and Tagus ValleyLisbon and Tagus ValleyLisbon and Tagus Valley